Torchvision在v0.11版本升级了许多内容,其中包括最新训练的基准模型,通过加入许多新的训练配置,极大的提高了原有的模型性能,比如将ResNet50从原来的76.130/92.862提升到80.858/95.434。这篇博文详细介绍了优化的过程 - How to Train State-Of-The-Art Models Using TorchVision’s Latest Primitives
使用 torchvision提供了多种加载预训练模型的方式,具体参考:Introducing TorchVision’s New Multi-Weight Support API 。示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from PIL import Image from torchvision import prototype as P img = Image.open("test/assets/encode_jpeg/grace_hopper_517x606.jpg") # Initialize model weights = P.models.ResNet50_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V2 model = P.models.resnet50(weights=weights) model.eval() # Initialize inference transforms preprocess = weights.transforms() # Apply inference preprocessing transforms batch = preprocess(img).unsqueeze(0) prediction = model(batch).squeeze(0).softmax(0) # Make predictions label = prediction.argmax().item() score = prediction[label].item() # Use meta to get the labels category_name = weights.meta['categories'][label] print(f"{category_name}: {100 * score}%")
具体实现变化很快,我看v0.13.0移除了prototype模块,各个模型定义和预训练权重路径都回到了原先的方式
1 2 3 weights = torchvision.models.resnet.ResNet50_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V2 model = torchvision.models.resnet.resnet50(weights=weights) model.eval()
训练 主要的配置选项如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 # Optimizer & LR scheme ngpus=8, batch_size=128, # per GPU epochs=600, opt='sgd', momentum=0.9, lr=0.5, lr_scheduler='cosineannealinglr', lr_warmup_epochs=5, lr_warmup_method='linear', lr_warmup_decay=0.01, # Regularization and Augmentation weight_decay=2e-05, norm_weight_decay=0.0, label_smoothing=0.1, mixup_alpha=0.2, cutmix_alpha=1.0, auto_augment='ta_wide', random_erase=0.1, ra_sampler=True, ra_reps=4, # EMA configuration model_ema=True, model_ema_steps=32, model_ema_decay=0.99998, # Resizing interpolation='bilinear', val_resize_size=232, val_crop_size=224, train_crop_size=176,
具体实现可以参考源码:vision/references/classification/ 。实现命令如下:
1 2 3 4 5 torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 train.py --model resnet50 --batch-size 128 --lr 0.5 \ --lr-scheduler cosineannealinglr --lr-warmup-epochs 5 --lr-warmup-method linear \ --auto-augment ta_wide --epochs 600 --random-erase 0.1 --weight-decay 0.00002 \ --norm-weight-decay 0.0 --label-smoothing 0.1 --mixup-alpha 0.2 --cutmix-alpha 1.0 \ --train-crop-size 176 --model-ema --val-resize-size 232 --ra-sampler --ra-reps 4
消融研究 针对ResNet50,各个训练trick的性能增益如下图所示:
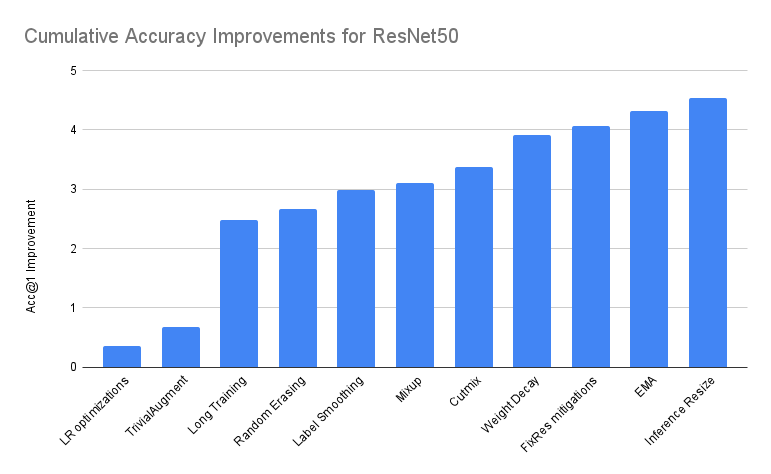
文章还通过表格形式展示了逐步添加各个trick后得到的结果以及对应的性能增益:
基准配置 首先是ResNet50的基准配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 # Optimizer & LR scheme ngpus=8, batch_size=32, # per GPU epochs=90, opt='sgd', momentum=0.9, lr=0.1, lr_scheduler='steplr', lr_step_size=30, lr_gamma=0.1, # Regularization weight_decay=1e-4, # Resizing interpolation='bilinear', val_resize_size=256, val_crop_size=224, train_crop_size=224,
后续文章详细介绍了依次增加各种训练配置获得的性能增益,在最后,文章还描述了大量经过测试但是没有得到性能提升的方法
小结 非常nice的一篇文章,发布了非常详细的数据,并且提供了详细的代码实现,对于工程实践绝对是宝藏!!!
通过学习大公司开源的实现,大部分人都可以获取得到最先进的技术,所有人都可以在同一个起跑线上,这个时候算法工程师的竞争力逐渐的不再是通用技术上的领先。我觉得,更多的应该专注于
如何掌握整个实现流程,不仅仅是训练,还包括数据处理、模型搭建、训练配置以及实际部署所有的环节;
如何更好的关联技术在业务上的实现。做计算机+,才能够有机会实现更强大的产品;
如何在业务上应用新的技术,这样才能够为社会提供更大的价值。