1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 19-4-18 上午9:22
# @Author : zj
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data_path = '../data/german.data-numeric'
def load_data(tsize=0.8, shuffle=True):
data_list = pd.read_csv(data_path, header=None, sep='\s+')
data_array = data_list.values
height, width = data_array.shape[:2]
data_x = data_array[:, :(width - 1)]
data_y = data_array[:, (width - 1)]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data_x, data_y, train_size=tsize, test_size=(1 - tsize),
shuffle=shuffle)
y_train = np.atleast_2d(np.array(list(map(lambda x: 1 if x == 2 else 0, y_train)))).T
y_test = np.atleast_2d(np.array(list(map(lambda x: 1 if x == 2 else 0, y_test)))).T
return x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test
def init_weights(inputs):
"""
初始化权重,符合标准正态分布
"""
return np.atleast_2d(np.random.uniform(size=inputs)).T
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-1 * x))
def logistic_regression(w, x):
"""
w大小为(n+1)x1
x大小为mx(n+1)
"""
z = x.dot(w)
return sigmoid(z)
def compute_loss(w, x, y):
"""
w大小为(n+1)x1
x大小为mx(n+1)
y大小为mx1
"""
lr_value = logistic_regression(w, x)
n = y.shape[0]
res = -1.0 / n * (y.T.dot(np.log(lr_value)) + (1 - y.T).dot(np.log(1 - lr_value)))
return res[0][0]
def compute_gradient(w, x, y):
"""
梯度计算
"""
n = y.shape[0]
lr_value = logistic_regression(w, x)
return 1.0 / n * x.T.dot(lr_value - y)
def compute_predict_accuracy(predictions, y):
results = predictions > 0.5
res = len(list(filter(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], np.dstack((results, y))[:, 0]))) / len(results)
return res
def draw(res_list, title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None):
if title is not None:
plt.title(title)
if xlabel is not None:
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
plt.plot(res_list)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载训练和测试数据
# train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = load_german_numeric(tsize=0.85, shuffle=False)
train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = load_data()
# 根据训练数据计算均值和标准差
mu = np.mean(train_data, axis=0)
std = np.std(train_data, axis=0)
# 标准化训练和测试数据
train_data = (train_data - mu) / std
test_data = (test_data - mu) / std
# 添加偏置值
train_data = np.insert(train_data, 0, np.ones(train_data.shape[0]), axis=1)
test_data = np.insert(test_data, 0, np.ones(test_data.shape[0]), axis=1)
# 定义步长、权重和偏置值
lr = 0.01
w = init_weights(train_data.shape[1])
# 计算目标函数/损失函数以及梯度更新
epoches = 20000
loss_list = []
accuracy_list = []
loss = 0
best_accuracy = 0
best_w = None
for i in range(epoches):
loss += compute_loss(w, train_data, train_label)
# 计算梯度
gradient = compute_gradient(w, train_data, train_label)
# 权重更新
tempW = w - lr * gradient
w = tempW
if i % 50 == 49:
# 每个50次记录一次
# 计算精度
accuracy = compute_predict_accuracy(logistic_regression(w, train_data), train_label)
accuracy_list.append(accuracy)
if accuracy > best_accuracy:
best_accuracy = accuracy
best_w = w.copy()
# 计算损失
loss_list.append(loss / 50)
loss = 0
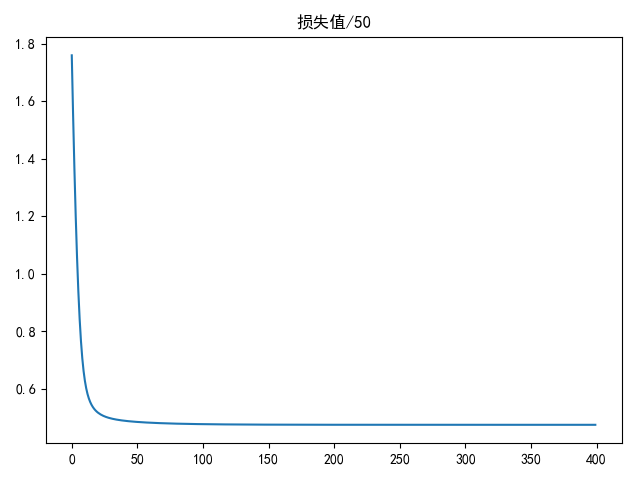
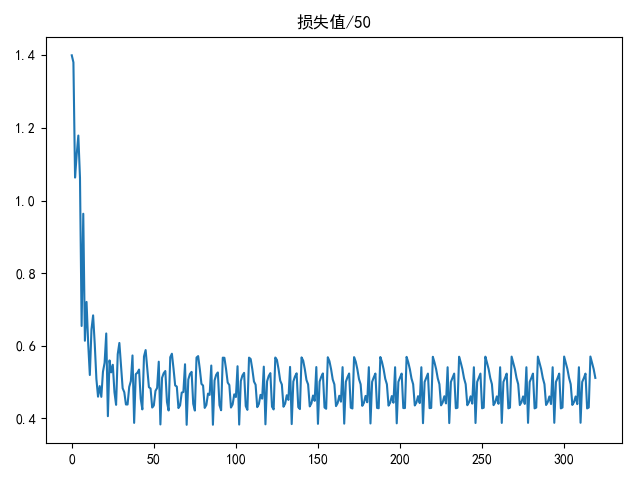
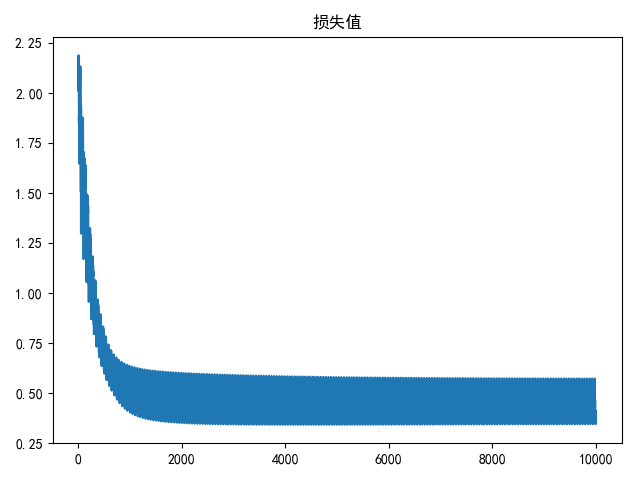
draw(loss_list, title='损失值/50')
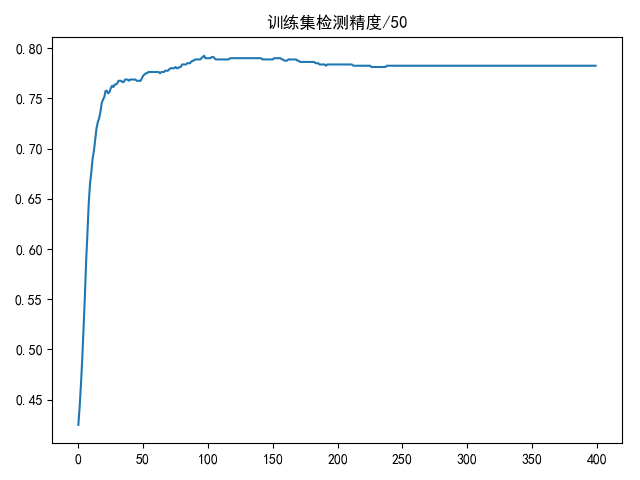
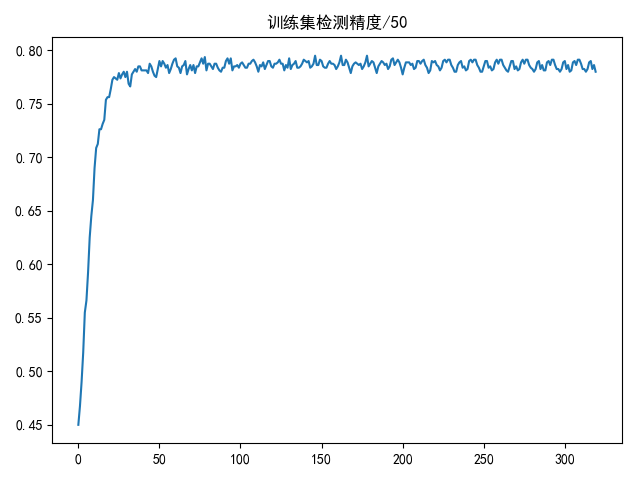
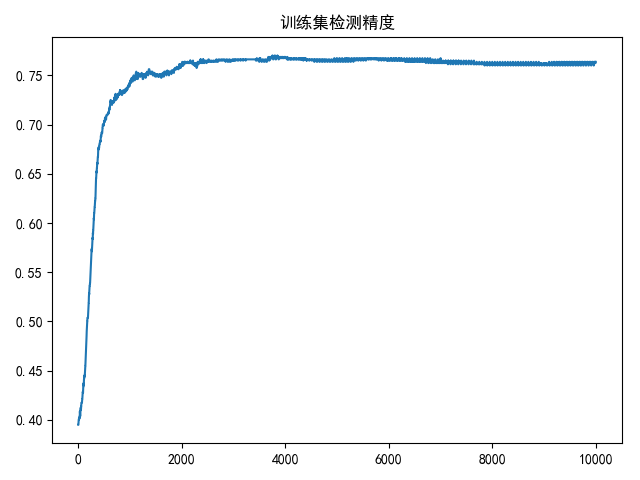
draw(accuracy_list, title='训练集检测精度/50')
print(max(accuracy_list))
print(compute_predict_accuracy(logistic_regression(best_w, test_data), test_label))
|